Suche
Beliebte Beiträge
-
 The Steve Jobs Of French Driving License Meet The Steve Jobs Of The French Driving License Industry
Durch licencefrancexpress5008
The Steve Jobs Of French Driving License Meet The Steve Jobs Of The French Driving License Industry
Durch licencefrancexpress5008 -
 The Ideal Scam Verification Platform for Korean Gambling Sites: Discover toto79.in
Durch valarie62m1160
The Ideal Scam Verification Platform for Korean Gambling Sites: Discover toto79.in
Durch valarie62m1160 -
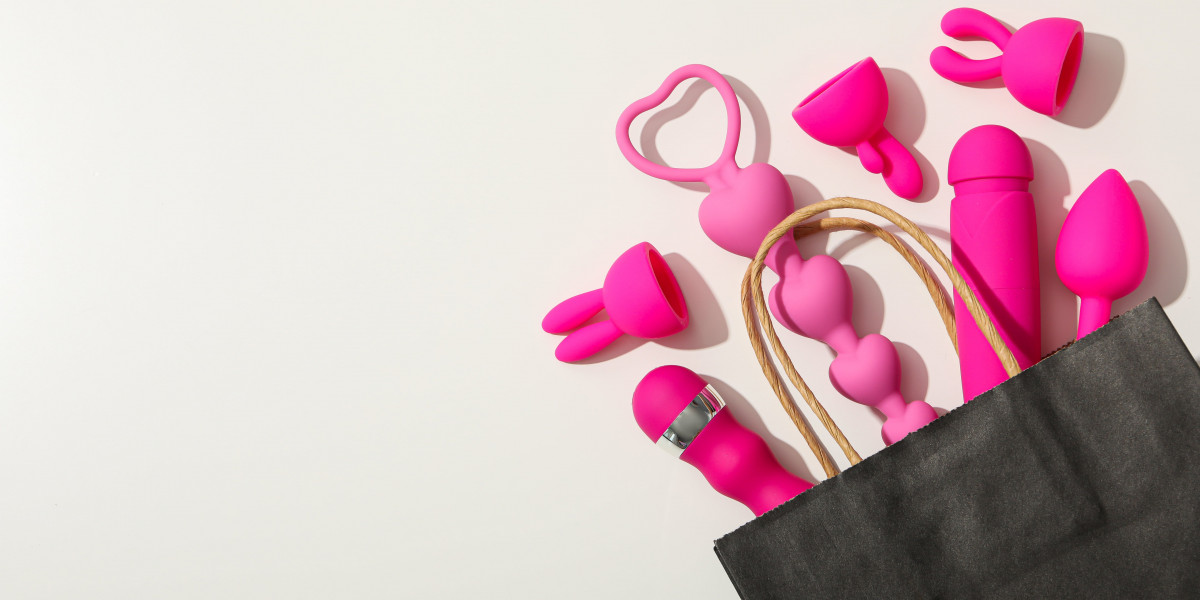 Exploring the World of Women's Adult Toys: A Comprehensive Guide
Durch topsadulttoys3420
Exploring the World of Women's Adult Toys: A Comprehensive Guide
Durch topsadulttoys3420 -
 Unveiling the Ultimate Destination for Togel Enthusiasts: The Largest Togel Site in Town
Durch petparrot8242
Unveiling the Ultimate Destination for Togel Enthusiasts: The Largest Togel Site in Town
Durch petparrot8242 -
 Unlocking the Secrets of Winning at Togel 4D: A Comprehensive Guide
Durch sifuromain5447
Unlocking the Secrets of Winning at Togel 4D: A Comprehensive Guide
Durch sifuromain5447
Kategorien




